
A Proactive Approach to Patient Management
Take a proactive approach to managing select adverse reactions (ARs)
There are measures you can take before and during treatment to be prepared to manage your patients. Select from the options below to learn more about how to plan, monitor, and manage certain ARs.

Please refer to the PIQRAY safety profile for additional ARs and the full Prescribing Information for additional monitoring and management guidance. The management plan of each patient should be based on the individual benefit/risk assessment.
Prior to treatment with PIQRAY:
Have a conversation with patients and assess their medical history before starting treatment
Prepare for potential ARs associated with PIQRAY by reviewing the Prescribing Information1
During treatment with PIQRAY:
Perform laboratory monitoring and regular assessment of your patient1
Advise patient of the potential serious and common ARs, their signs and symptoms, and to contact their HCP immediately should any occur1

Monitoring AR Checklist
Monitor for ARs before and during treatment with this checklist intended for all members of the oncology care team.
If an AR does occur:
Adjust monitoring schedule according to the PIQRAY Prescribing Information1
Refer to the AR management guidance from SOLAR-1 in the PIQRAY Prescribing Information
Explore treatment considerations for select ARs
Select from the options below to learn more about monitoring considerations for serious and common ARs that may occur during treatment. As part of taking a proactive approach for managing your patients on PIQRAY, it's important to know what steps you can take before prescribing, recommendations for monitoring, and how ARs were managed in SOLAR-1. General guidelines for select ARs are summarized in the tabs below. For more information, please refer to the PIQRAY Prescribing Information.
Before treatment with PIQRAY
![]()
Consider prophylaxis with antihistamines prior to onset of rash
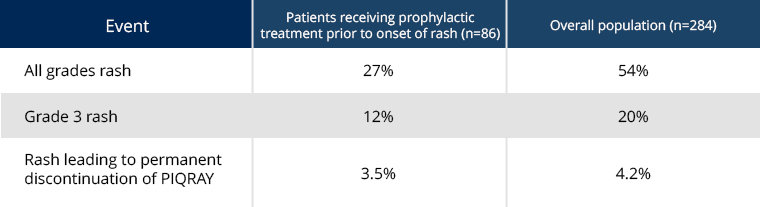
Antihistamines administered prior to rash onset may decrease incidence and severity of rash based on a subgroup analysis of patients in the SOLAR-1 trial1
Effects of prophylactic treatment, including antihistamines, prior to onset of rash in patients receiving PIQRAY + fulvestrant1
During treatment with PIQRAY
![]() Advise patients of the signs and symptoms of severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARs) and to immediately contact their health care provider should they occur1
Advise patients of the signs and symptoms of severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARs) and to immediately contact their health care provider should they occur1
A prodrome of fever, flu-like symptoms, mucosal lesions, progressive skin rash, or lymphadenopathy1
![]() Monitor for different forms of rash
Monitor for different forms of rash
Rash may present as rash, rash maculopapular, rash macular, rash generalized, rash papular, rash pruritic, and maculopapular rash (one of the most common)1,2
Rash in SOLAR-1
Most events were mild to moderate (grade 1 or 2). 52% of patients experienced all-grades rash with 20% reporting grade 31
Median time to first onset of grade 2 or 3 rash

12 days (range 2-220 days)1
If a patient experiences severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARs) or rash:
If a SCAR is confirmed, permanently discontinue PIQRAY. Do not reintroduce PIQRAY in patients who have experienced previous SCAR during treatment1
Refer to the Prescribing Information for management recommendations and medication used for rash in the SOLAR-1 trial
Before treatment with PIQRAY
![]()
Assess fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), and optimize blood glucose1
In the SOLAR-1 trial, patients with controlled type 2 diabetes and prediabetes were included if they had an FPG of ≤140 mg/dL (7.7 mmol/L) and HbA1c of ≤6.4% (both criteria had to be met)2
![]() Assess patient's past medical history1
Assess patient's past medical history1
The safety of PIQRAY in patients with type 1 and uncontrolled type 2 diabetes has not been established as these patients were excluded from SOLAR-1. Patients with a medical history of controlled type 2 diabetes were included1
Patients with a history of diabetes mellitus may require intensified hyperglycemic treatment. Closely monitor patients with diabetes1
![]() Have a prescription ready for metformin in the event that your patient experiences hyperglycemia
Have a prescription ready for metformin in the event that your patient experiences hyperglycemia
87% of patients (163/187) were managed with antihyperglycemic medication in the SOLAR-1 trial; 76% (142/187) used metformin as a single agent or in combination with other antihyperglycemic medications1
![]() Consider prescribing a glucometer when starting patients on PIQRAY to begin regular monitoring of fasting glucose at home
Consider prescribing a glucometer when starting patients on PIQRAY to begin regular monitoring of fasting glucose at home
Including a glucometer prescription will ensure that your patients can do the required fasting glucose monitoring on a regular basis, with more frequent monitoring for patients with risk factors for hyperglycemia and at your clinical discretion1*
*Risk factors include obesity (BMI ≥30), elevated FPG, HbA1c at the upper limit of normal or above, use of concomitant systemic corticosteroids, or age ≥75. In addition to FPG, HbA1c levels should be monitored. Please refer to the PIQRAY Prescribing Information for recommended monitoring intervals.
BMI, body mass index.
During treatment with PIQRAY
![]() Test FPG or fasting blood glucose as recommended1
Test FPG or fasting blood glucose as recommended1
Monitor more frequently for the first few weeks during treatment in patients with risk factors for hyperglycemia such as obesity (BMI ≥30), elevated FPG, HbA1c at the upper limit of normal or above, use of concomitant systemic corticosteroids, or age ≥75
![]() Advise patients of signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia and to contact their health care provider immediately should they occur1
Advise patients of signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia and to contact their health care provider immediately should they occur1
Excessive thirst, urinating more often than usual or higher amount of urine than usual, or increased appetite with weight loss1
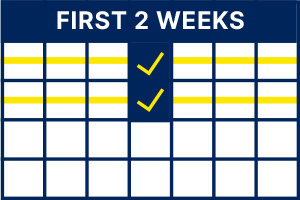
First 2 weeks:
At least 1x per week1
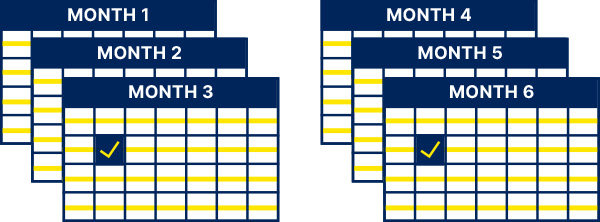
After the first 2 weeks:
At least once every 4 weeks and as clinically indicated for the duration of treatment1

Test HbA1c:
Once every 3 months and as clinically indicated for the duration of treatment1
HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin.
If hyperglycemia occurs, adjust monitoring schedule
Monitor fasting glucose as clinically indicated, and at least 2x per week until fasting glucose decreases to normal levels1
Consider consultation with a health care provider with expertise in the treatment of hyperglycemia and counsel patients on lifestyle changes, such as diet modifications and increased exercise, as a part of hyperglycemia management1
During treatment with anti-hyperglycemic medication, adjust monitoring schedule. Monitor FPG or fasting blood glucose at least once a week for 8 weeks, followed by once every 2 weeks and as clinically indicated1
Glucose increase, including hyperglycemia, is an expected, on-target effect of PI3K inhibition1,3
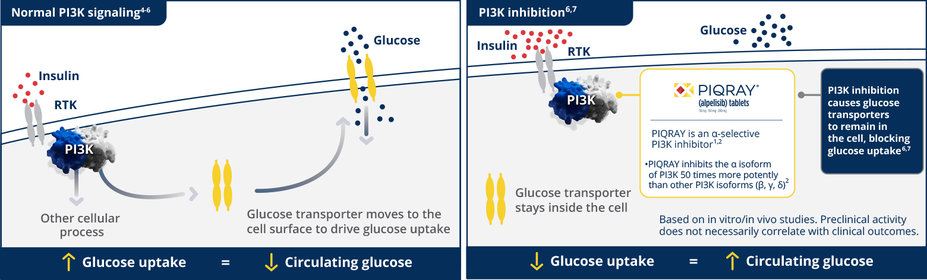
65% of patients treated with PIQRAY in SOLAR-1 reported hyperglycemia1
Severe hyperglycemia, in some cases associated with hyperglycemic hyperosmolar non-ketotic syndrome (HHNKS) or ketoacidosis has occurred in patients treated with PIQRAY. Fatal cases of ketoacidosis have occurred in the postmarketing setting1
Grade 3 (FPG >250-500 mg/dL): 33% and Grade 4 (FPG >500 mg/dL): 3.9%
—Glucose increase (all grades) was reported in 79% of patients treated with PIQRAY + fulvestrant
Median time to first occurrence of grade ≥2 (FPG 160-250 mg/dL) hyperglycemia

15 days (range 5-517 days)1
FPG, fasting plasma glucose.
Based on the severity of the hyperglycemia, PIQRAY may require dose interruption, reduction, or discontinuation1
During treatment with PIQRAY
In SOLAR-11
Severe diarrhea, resulting in dehydration and in some cases in acute kidney injury, can occur in patients treated with PIQRAY
58% of patients experienced diarrhea during treatment with PIQRAY + fulvestrant
— 7% (n=19) of patients had grade 3 diarrheaColitis has been reported in the postmarketing setting in patients treated with PIQRAY
Median time to onset of grade 2 or 3 diarrhea (n=71): 46 days (range: 1-442 days)
— 63% of patients who experienced diarrhea required antidiarrheal medications (eg, loperamide) to manage symptomsDose reductions of PIQRAY were required in 6% of patients, and 2.8% of patients permanently discontinued PIQRAY due to diarrhea
Median time to onset of grade 2 or 3 diarrhea

46 days (range, 1 to 442 days)1
Based on the severity of the diarrhea, PIQRAY may require dose interruption, reduction, or discontinuation1
